
- #UBUNTU WRITE ISO TO USB HOW TO#
- #UBUNTU WRITE ISO TO USB INSTALL#
- #UBUNTU WRITE ISO TO USB WINDOWS#
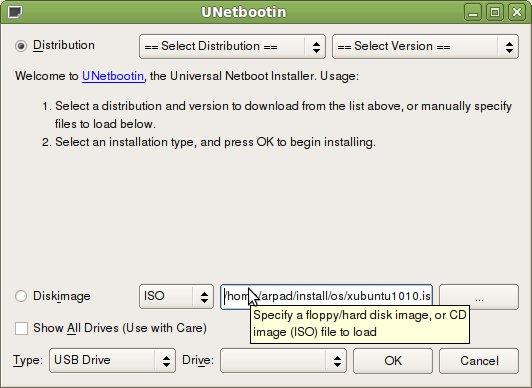
Locate your Ubuntu ISO file and then click Open.įrom the Device drop-down list, select the device drive of your USB flash drive. In the file type drop-down list, select *.* so you can see all files, regardless of file extension.
#UBUNTU WRITE ISO TO USB INSTALL#
#UBUNTU WRITE ISO TO USB HOW TO#
Here's how to use it to create a UEFI bootable Ubuntu USB drive: IMG files to SD and USB cards and allow booting from these devices. Win32 Disk Imager is a simple disk imaging utility to write. Method 2: Create UEFI Bootable Ubuntu USB Drive Using Win32 Disk Imager Wait for the burning process to be completed. Start the ISO2Disc application, then click the Browse button to locate the Ubuntu ISO file you've downloaded.Ĭlick the " Burn to USB Flash Drive" option, choose the USB drive attached to your computer, and then select " GPT (required for UEFI boot)" partition style.Download the freeware ISO2Disc and install it on your Windows-based computer.Just grab a copy of Ubuntu ISO file and you can simply create a UEFI bootable USB drive. ISO2Disc is a lightweight yet powerful freeware designed to create bootable CD or USB drive from ISO image. Method 1: Create UEFI Bootable Ubuntu USB Drive Using ISO2Disc A USB flash drive (at least 2GB is recommended).64-bit (AMD64) desktop image of Ubuntu 12.0.4 LTS or higher.
#UBUNTU WRITE ISO TO USB WINDOWS#
In this tutorial we'll show you 2 simple ways to create a UEFI bootable Ubuntu USB drive in Windows 10, 8 and 7. We recommend using Ubuntu 12.04 LTS 64-bit or higher. So, you might want to read about how to create verified OpenBSD installation media on Linux and integrate that into the process.Can I install Ubuntu with UEFI mode? How to create UEFI-only bootable USB drive from Ubuntu ISO image? Ubuntu supports 圆4 UEFI for 64-bit builds, starting with 10.10. Etcher will autoselect the USB drive if only one drive is present. If you downloaded the file using a web browser, then it should be stored in the Downloads folder located in your user account.

Click on the Select image button and locate your CentOS. Last but not least, I wouldn't install a system using an installation image that I haven't verified in any way. Insert the USB flash drive into the USB port on your computer and Launch Etcher. If you get your shell prompt back without any errors printed, everything should be fine.
Now, here's how to get an OpenBSD image onto a USB flash device (aka USB key) on Linux:ĭownload the appropriate *.fs file, e.g., install67.fs, not the *.iso variant. It's a standard command on Unix(-like) systems. What would the statement be to create a bootable USB for OpenBSD?įirst things first, dd(1) is not part of Bash. "Ubuntu 18.04" might be the name of my previous iso file which can be deleted. If my iso file is located on my home path so: And it seems to be different on each system.

The explanation on how to use "dd" statement is unclear to me. But the iso file is not selected because "Startup disk creation" could only be used for Ubuntu.īut the bash dd command could be used. On the new system I use Ubuntu 18.04 and I want to use "Startup disk creation" and try select the. So I used my new system and went to and downloaded "instal67.iso" successful. Firefox can not access to Internet anymore because the security protocol is enabled. I did not use this for a long time and now I want to install OpenBSD on this system. I have a very old system using Ubuntu 4.04 with Firefox 2.0.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
